ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
Sub-strand 3.1: Generation, Transmission, and Distribution of Electricity
- Methods of Generation of Electrical Energy:
- Thermal Power Plants: Burn fossil fuels (coal, natural gas) to produce steam, which drives turbines connected to generators.
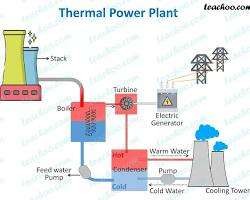
Thermal power plant
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: Use the kinetic energy of falling water to drive turbines connected to generators.

Hydroelectric dam
- Nuclear Power Plants: Use nuclear fission to generate heat, which produces steam to drive turbines connected to generators.
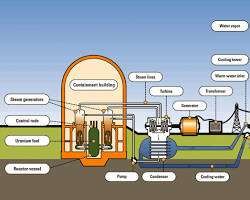
Nuclear power plant
- Wind Power Plants: Use wind turbines to convert wind energy into electrical energy.

Wind turbine farm
- Solar Power Plants: Use photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight directly into electrical energy.

Solar power plant
- Geothermal Power Plants: Use heat from the Earth’s interior to produce steam, which drives turbines connected to generators.
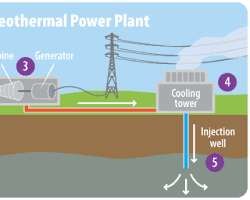
Geothermal power plant
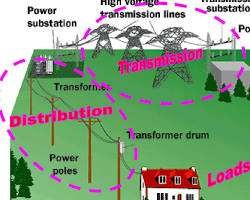
- Functions of Components in the Electrical Power Transmission Network:
- Generators: Convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.

Electrical generator
- Transformers: Step up voltage for efficient transmission and step down voltage for distribution.

high voltage transformer
- Transmission Lines: Carry high-voltage electricity over long distances.

high voltage transmission towers
- Substations: Contain transformers, switchgear, and other equipment for voltage transformation and distribution.

Electrical substation
- Distribution Lines: Carry lower-voltage electricity to consumers.
Distribution power lines
- Circuit Breakers and Switches: Protect the system from faults and allow for isolation of sections.

Circuit breaker panel
- 3-Phase 4-Wire Distribution Circuit:
- A 3-phase 4-wire system provides three phase lines and a neutral line.
- Used for distributing power to residential and commercial consumers.
- Phase symmetry ensures balanced loads.
- Line-to-line voltage is higher than line-to-neutral voltage.
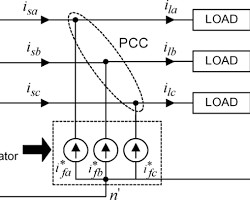
3-phase 4wire distribution diagram
- Electric Power Grid Network Model:
- A power grid is an interconnected network of generation, transmission, and distribution systems.
- Models can be created using diagrams, simulations, or physical representations. Models help visualize the flow of electricity and identify critical components.
simplified power grid diagram
- Importance of a Grid System:
- Ensures reliable and continuous power supply.
- Allows for efficient distribution of electricity over large areas.
- Enables load balancing and sharing of resources.
- Supports economic development and industrial growth.
- Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources.
Map showing a countries power grid Sub-strand 3.2: Equipment at Consumers Intake Point
- Identifying Equipment at Consumers Electrical Power Intake Point:
- The consumer’s intake point is where the electrical supply from the distribution network enters the building.
- Common equipment includes:
- Isolation switch (main switch)
- Electricity meter
- Circuit breakers (main circuit breaker)
- Cartridge fuses
- Consumer control unit (distribution board/consumer unit) Earthing terminal

Electrical meter
- Functions of Control Equipment:
- Isolation switch (main switch):
- Provides a means to completely disconnect the electrical supply for maintenance or emergencies.
- Isolation switch (main switch):

Isolation switch
- Electricity meter:
- Measures the amount of electrical energy consumed.

Electricity meter
- Circuit breakers (main circuit breaker):
- Protect the installation from over-currents and short circuits.

Circuit breaker
- Cartridge fuses:
Provide backup protection against over-currents.

Cartridge fuse
- Consumer control unit (distribution board/consumer unit):
Distributes the electrical supply to individual circuits within the building. Contains circuit breakers or fuses for each circuit.

Consumer control unit opened
- Installing Control Equipment in the Correct Sequence:
- The correct sequence ensures proper protection and operation.
- Typical sequence:
o Isolation switch → Electricity meter → Main circuit breaker/fuses → Consumer control unit.
Download more notes 2026 Grade 10 Notes Senior School Term1 2 and 3

